
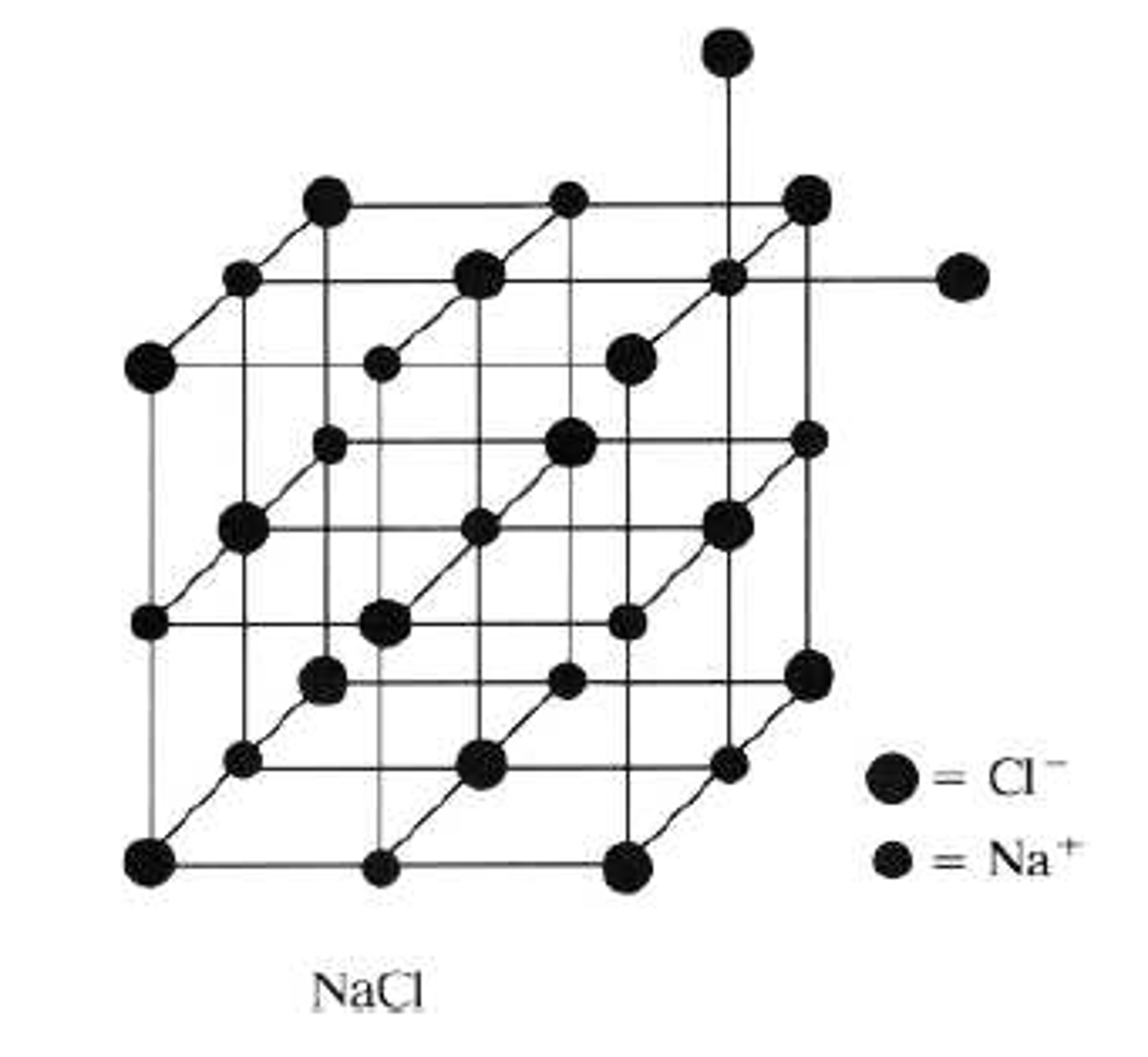
And if you're lucky, you might get some beautiful symmetric crystals like these. Salt that you might have, dissolve it up in some water, and then let that water slowly evaporate. So here we have a close-up picture of some really niceĬrystals of sodium chloride. An example of a compound that's held together with ionic bonds is sodium chloride, also Ionic bonds are the bonds that hold together ionic compounds. Nonetheless, NaCl is said to dissolve in water, because evaporation of the solvent returns crystalline NaCl. When, however, an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolves in water, the sodium chloride lattice dissociates into separate ions which are solvated (wrapped) with a coating of water molecules. When ethanol dissolves in water, the ethanol molecules remain intact but form new hydrogen bonds with the water. The process of dissolving, called dissolution, is relatively straightforward for covalent substances such as ethanol. The term insoluble is often applied to poorly soluble compounds, though strictly speaking there are very few cases where there is absolutely no material dissolved. Solubilities range widely, from infinitely soluble such as ethanol in water, to poorly soluble, such as silver chloride in water.

The species that dissolves, the solute, can be a gas, another liquid, or a solid. The solvent is often a solid, which can be a pure substance or a mixture. Under various conditions, the equilibrium solubility can be exceeded to give a so-called supersaturated solution, which is metastable. The resulting solution is called a saturated solution.Ĭertain substances are soluble in all proportions with a given solvent, such as ethanol in water. It is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a solvent at equilibrium. Solubility is a chemical property referring to the ability for a given substance, the solute, to dissolve in a solvent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
